Gout: Causes, Symptoms, and Natural Remedies
Gout is a form of arthritis caused by the buildup of uric acid in the bloodstream, which leads to the formation of sharp uric acid crystals in the joints. Uric acid is a byproduct of the breakdown of purines, substances found in many foods. When the body cannot effectively eliminate uric acid through urine, it crystallizes in the joints, causing intense pain and inflammation.
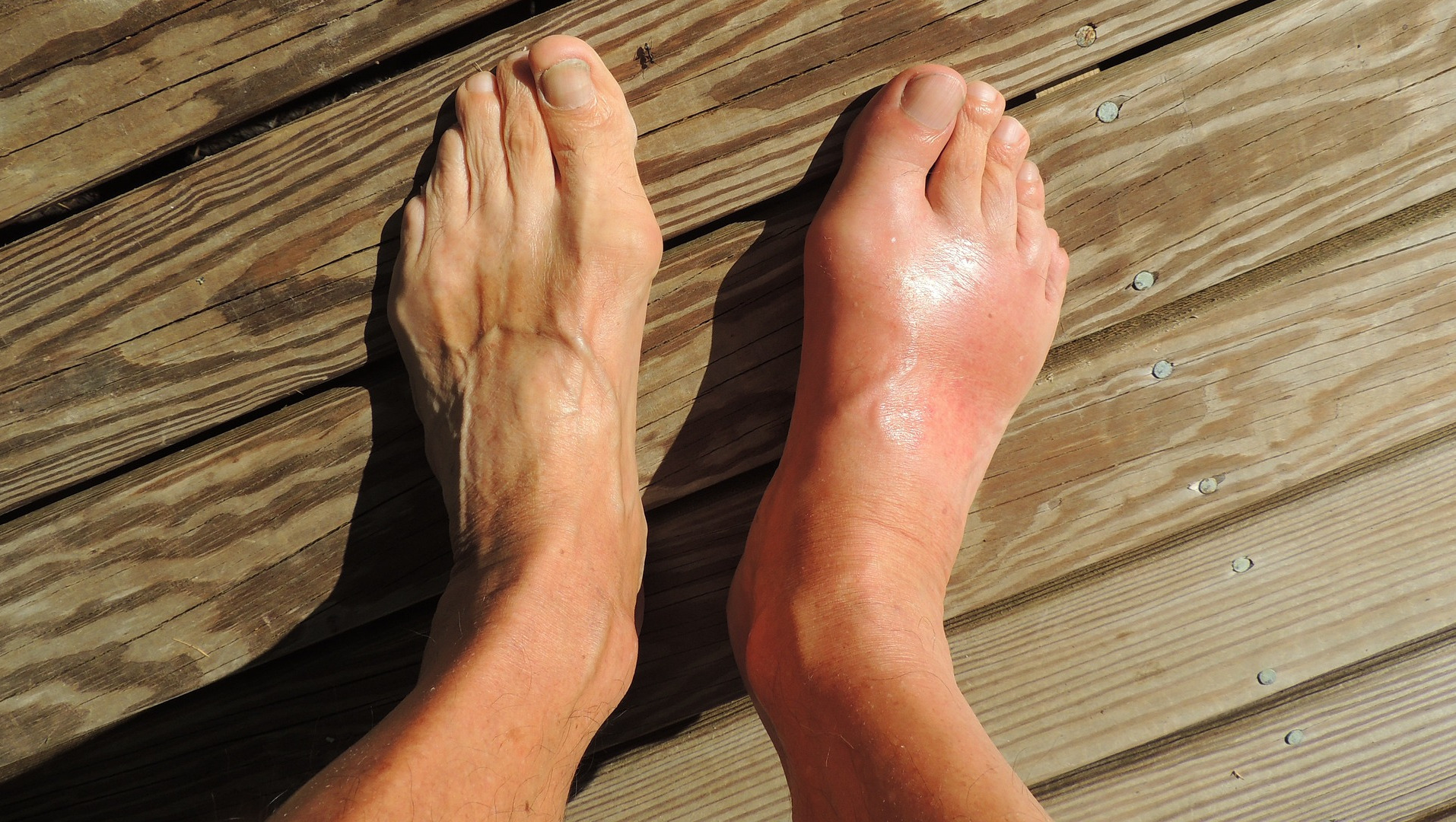
Gout most commonly affects the big toe but can also affect the ankles, knees, and other joints. Left untreated, gout can lead to permanent joint damage and even kidney problems.
Common Causes of Gout
- High-purine diet: Foods rich in purines, such as red meat, organ meats, and certain seafood, contribute to excess uric acid production.
- Genetics: Some people are genetically predisposed to poor uric acid metabolism.
- Medications: Some antibiotics and diuretics may increase uric acid levels.
- Alcohol consumption: Alcohol, especially beer, is high in purines and can also interfere with the body's ability to eliminate uric acid.
- Obesity: Being overweight increases the risk of developing gout, hindering the body's ability to process uric acid efficiently.
Symptoms of Gout
- Intense joint pain, often at the base of the big toe
- Swelling, redness, and warmth in the affected joint
- Shiny, tight skin over the joint
- Pain that worsens with movement
Foods to Avoid for Gout Prevention
To reduce the risk of gout flare-ups, avoid the following high-purine foods:
- Organ meats (liver, kidney)
- Shellfish and small fish (anchovies, sardines, mackerel)
- Alcohol, especially beer
- Sugary drinks and foods high in fructose (soda, sweets)
Home Remedies and Natural Cures for Gout
Gout is a painful and often chronic condition, but it can be managed effectively with the right combination of diet, herbal remedies, and lifestyle changes. By avoiding high-purine foods, staying hydrated, and incorporating natural anti-inflammatory remedies into your daily routine, you can reduce the frequency and severity of gout attacks. In cases of chronic gout or severe flare-ups, seeking medical treatment is essential to prevent long-term joint damage or kidney complications.
While medication is often necessary to manage gout, there are several home remedies and lifestyle changes that can help prevent attacks and reduce symptoms.
Nutrition and Hydration
One of the most important ways to manage and prevent gout is by adjusting your diet:
- Avoid high-purine foods: Limit or avoid foods high in purines, such as anchovies, sardines, liver, kidney, mussels, and yeast. Additionally, avoid processed meats and sugary beverages, which can trigger gout attacks.
- Eat more low-purine foods: Focus on foods like fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and low-fat dairy, which are safe for gout sufferers.
- Stay hydrated: Drink plenty of water throughout the day to help flush out excess uric acid and prevent crystal formation.
- Avoid alcohol: Especially beer, which is high in purines and can worsen gout symptoms.
Herbal Remedies
Several herbs can help reduce inflammation and support uric acid metabolism:
- Peperomia pellucid: This herb is commonly used to treat gout and arthritis. Its anti-inflammatory properties make it a good choice for tea. Boil chopped leaves in water to make a tea, and drink a cup after meals.
- Yerba Buena (mint family): Traditionally used as an analgesic, it can help relieve joint pain. Boil the leaves, strain, and drink a cup every few hours to reduce pain and swelling.
- Blumea Camphora: A diuretic herb that increases urination and helps flush out excess uric acid. It can be brewed into tea and consumed several times daily to reduce uric acid buildup and prevent kidney stones.
Cherries and Berries
Cherries and other dark berries, such as blueberries and strawberries, are rich in anthocyanins, which have anti-inflammatory properties. Eating cherries or drinking cherry juice can help lower uric acid levels and reduce the frequency of gout attacks.
Lemon Juice
Lemons are alkaline and help neutralize uric acid in the body. Drinking a glass of lemon water (fresh lemon juice mixed with water) every morning can help balance uric acid levels and prevent crystal formation.
Apple Cider Vinegar
Apple cider vinegar has been praised for reducing inflammation and balancing pH levels. Mix one to two tablespoons of raw, organic apple cider vinegar in a glass of water and drink it daily to help manage gout symptoms.
Turmeric
Turmeric contains curcumin, a compound with potent anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties. Adding turmeric to your diet or taking a turmeric supplement can help reduce inflammation and prevent gout flare-ups.
Ginger
Ginger is another potent anti-inflammatory that can help relieve joint pain associated with gout. It can be consumed as a tea or added to meals. You can also make a ginger compress by boiling fresh ginger in water, soaking a cloth in the solution, and applying it to the affected area to relieve pain.
Cold Compress
Applying a cold compress to the inflamed joint can help reduce swelling and numb the pain. Use an ice pack or a cloth-wrapped ice cube and apply it to the affected joint for 10-15 minutes daily.
Exercise and Weight Management
Regular exercise and maintaining a healthy weight can help reduce the frequency of gout attacks. Excess weight stresses the joints and increases the risk of uric acid buildup. To stay active without stressing your joints, engage in low-impact activities like walking, swimming, or cycling.
Medications and Supplements
For those experiencing acute gout attacks or chronic gout, medications may be necessary:
- NSAIDs (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs): Medications like ibuprofen can help reduce pain and inflammation during a gout attack.
- Colchicine: This medication helps reduce the swelling and pain associated with gout.
- Allopurinol or Febuxostat: These medications are prescribed to lower uric acid levels and prevent future gout attacks.